The ear is the sense organ for hearing and balance (equilibrium).
Not only does the ear act as a receiver for sound it also plays a major role in the sense of position and balance. All humans have two ears but some animals have no ears at all… like snakes! Snakes use their tongues to receive and interpret sound vibrations.
What is sound?
Sound is a form of energy that moves through air, water and matter, in waves of pressure. While the ear recognizes sound it is the brain and central nervous system that “hears”. The ear and the brain work together. The ear changes sound pressure waves from the outside world into signals of nerve impulses which are then sent to the brain.
What is an ear made up of?
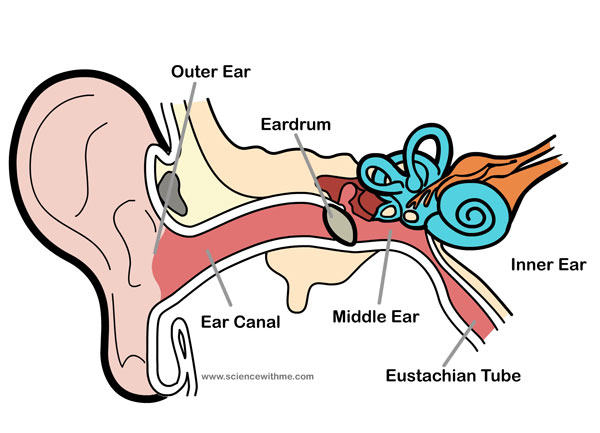 Outer ear: The visible external ear is called the pinna or auricle. This is the part of the ear that humans sometimes ornament with jewellery. The outer ear also contains the ear canal and the ear drum (tympanic membrane). The middle ear: is the area behind the ear drum. This part of the ear is made of three movable bones called ossicles. The function of these three bones is to convert the sound wave (by striking the eardrum) into mechanical vibrations. These three bones are absolutely tiny and are the smallest bones in the body! The hammer (Malleaus) – joins the inside of the eardrum. The anvil (Incus) – connects to the hammer and the stirrup. The stirrup (Staples) – fills the oval window (membrane covered outlets) which leads to the inner ear.
Outer ear: The visible external ear is called the pinna or auricle. This is the part of the ear that humans sometimes ornament with jewellery. The outer ear also contains the ear canal and the ear drum (tympanic membrane). The middle ear: is the area behind the ear drum. This part of the ear is made of three movable bones called ossicles. The function of these three bones is to convert the sound wave (by striking the eardrum) into mechanical vibrations. These three bones are absolutely tiny and are the smallest bones in the body! The hammer (Malleaus) – joins the inside of the eardrum. The anvil (Incus) – connects to the hammer and the stirrup. The stirrup (Staples) – fills the oval window (membrane covered outlets) which leads to the inner ear.
The inner ear
Cochlea – is a snail-shell like structure divided into three fluid-filled parts. Cilia – Microscopic hair-like structures. Eustachian Tube – This tube equalises air pressure. It also connects the middle ear to the throat and this is where most ear infections happen. This tube is normally collapsed but it opens up when we are swallowing food or with any pressure, such as taking off in an aeroplane, giving the sensation of popping.
How do we hear?
The outer part of the ear collects sound waves. Humans can hear sound waves with frequencies between 20 and 20,000 Hz. That sound pressure is amplied through the middle portion of the ear. In simple language these sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate. The three middle ear bones (Malleaus, Incus, Staples or easier to remember Hammer, Anvil and Stirrup) pass these vibrations on to the cochlea. The cochlea is a snail-shaped, fluid-filled structure in the inner ear. Inside the cochlea is another structure called the organ of corti. Cilia are very tiny hair cells which are located in the corti. These cilia (microscopic hair cells) bend over from the vibrations (sound waves) passing a nerve impulse to the auditory nerve. These impulses are then sent to the brain and this is how we hear sounds.
Why do we get dizzy when we spin around?
When you spin around too fast, fluid in the circular canals (cochlea) moves around the ear. This stimulates the hair cells. When you stop spinning the fluid still moves. Because the moving fluid is still stimulating the hair cells your brain gets a message that you are still moving and so you feel dizzy.
Why are ears so important to us?
The ability to hear and balance is very important to all living creatures. For humans hearing is also an important part of learning speech and language so we can communicate with each other. So, we must protect our hearing. Exposure to loud noise, whether instant or prolonged, can cause damage to these hair cells as they become brittle and don’t bounce back into shape. When this happens we get a constant hum in our ears called Tinnitus. Some cases of tinnitus are caused by too much ear wax or infection but mostly it is caused by loud music or noise. This is why we must be careful not to expose ourselves to too much loud noise as excessive noise is still the number one reason for hearing loss. Sound loudness is measured in decibels (dB). A whisper is 30 db but a Lawn mower is 95 (dB). Prolonged exposure to anything over 80 dB can cause hearing damage. So turn down those MP3 players kids!
Interesting Facts
-
The staples is the smallest bone in the whole body! It is only 0.25 to 0.33 cm long and only weighs 1.9 to 4.3 milligrams.
-
200,000 people in the United States are deaf; 3 million people in the US have serious hearing problems.
-
Fish do not have ears, but they can hear. They hear pressure changes through ridges on their bodies.
-
Crickets have their hearing organs in their knees!
